1.3.a (i) debug, conditional debug
1.3.a (ii) ping, traceroute with extended options
1.3.a (iii) Embedded packet capture
1.3.a (iv) Performance monitor
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/media_monitoring/configuration/15-mt/mm-15-mt-book/mm-pasv-mon.html
Overview of Cisco Performance Monitor
Because Cisco Performance Monitor uses similar software components and commands as Cisco NetFlow and Cisco Flexible NetFlow, familiarity with these products will help you to understand how to configure Cisco Performance Monitor. These products provide statistics on packets flowing through a router and are the standard for acquiring IP operational data from IP networks. They provide data to support network and security monitoring, network planning, traffic analysis, and IP accounting. For more information about Cisco NetFlow and Cisco Flexible NetFlow, see the documents listed in the Additional References section.
Prerequisites for Configuring Cisco Performance Monitor
IPv4 Traffic
IPv6 Traffic
Configuration Components of Cisco Performance Monitor
The figure below shows how these elements are related to each other. The elements at the bottom of the figure are configured first.
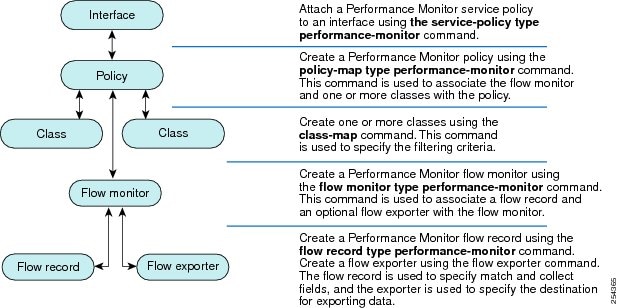
- Configure a flow record to specify the key and non-key fields that you want to monitor. This is configured using match and collect commands. You can also optimally configure a flow exporter to specify the export destination. For Cisco Performance Monitor, you must configure a performance-monitor type flow record.
- Configure a flow monitor that includes the flow record and flow exporter. For Cisco Performance Monitor, you must configure a performance-monitor type flow monitor.
- Configure a class to specify the filtering criteria using the class-map command.
- Configure a policy to include one or more classes and one or more performance-monitor type flow monitors using the policy-map command. For Cisco Performance Monitor, you must configure performance-monitor type policies.
- Associate a performance-monitor type policy to the appropriate interface using the service-policy type performance-monitor command.
Data That You Can Monitor Using Cisco Performance Monitor
 Tip | For more information about these statistics, see the show performance monitor statuscommand in theCisco Media Monitoring Command Reference. |
- IP Packet Count
- IP TTL
- IP TTL minimum
- IP TTL maximum
- Flow to Interface Mapping
- IP Flow destination address and port, source address and port, and protocol
- RTP Synchronization Source (SSRC)
- IP Octets Count
- Media Stream Packet Count
- Media Stream Octect Count
- Media Byte Rate
- Media Byte Count
- Media Packet Rate
- Media Packet Loss Count
- Media Packet Loss Rate
- Packets Expected Count
- Measured Rate
- Media Loss Event Count
- Round Trip Time (RTT)
- Interarrival Jitter (RFC3550) max
- Interarrival Jitter (RFC3550) min 2
- Interarrival Jitter (RFC3550) mean
- Media Rate Variation
- Monitor Event
- Media Error
- Media Stop
- IP Byte Count
- IP Byte Rate
- IP Source Mask
- IP Destination Mask
- Epoch of A Monitoring Interval
- Packet Forwarding Status
- Packet Drops
- DSCP and IPv6 Traffic Class
SNMP MIB Support for Cisco Performance Monitor
- CISCO-FLOW-MONITOR-TC-MIB—Defines the textual conventions common to the following MIB modules.
- CISCO-FLOW-MONITOR-MIB—Defines the framework that describes the flow monitors supported by a system, the flows that it has learned, and the flow metrics collected for those flows.
- CISCO-RTP-METRICS-MIB—Defines objects that describe the quality metrics collected for RTP streams, similar to those described by an RTCP Receiver Report packet (RFC 3550).
- CISCO-IP-CBR-METRICS-MIB—Defines objects that describe the quality metrics collected for IP streams that have a Constant Bit Rate (CBR).
This feature also includes two new command-line interface (CLI) commands and one modified CLI command. The commands are as follows:
- snmp-server host—Enables the delivery of flow monitoring SNMP notifications to a recipient.
- snmp-server enable traps flowmon—Enables flow monitoring SNMP notifications. By default, flow monitoring SNMP notifications are disabled.
- snmp mib flowmon alarm history—Sets the maximum number of entries maintained by the flow monitor alarm history log.
No comments:
Post a Comment